Introduction to Darkroom Ventilation and Safety
Welcome to the world of darkroom photography! It's a rewarding craft, but also one that demands respect for the materials and processes involved. This article provides a crucial introduction to darkroom ventilation and safety, ensuring a comfortable and safe environment for developing and printing your black and white photographs. Neglecting these aspects can lead to health problems and an unpleasant working experience. The darkroom environment can be quite specific in its needs, and understanding these needs is key to creating high-quality prints and avoiding potential hazards.
Why is Ventilation So Important?
Developing and printing black and white film involves a range of chemicals, many of which emit fumes. These fumes, even at low concentrations, can be irritating to the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Prolonged exposure can lead to more serious health concerns. Proper ventilation removes these fumes, keeping the air in your darkroom clean and breathable. Beyond just breathing easier, safe lighting is also paramount. Ensuring you have safe lighting for darkroom photography is essential for your eyesight and general wellbeing during the process of creating an image.

Understanding the Chemicals – A Quick Overview
Let’s briefly touch on some common darkroom chemicals and their associated hazards:
- Developer: Typically contains reducing agents. While less immediately hazardous than some other chemicals, proper ventilation is still essential.
- Stop Bath: Usually an acidic solution. Can cause irritation to skin and eyes.
- Fixer: Contains chemicals that dissolve the unexposed silver halide crystals. Fumes can be irritating. Knowing the intricacies of fixing your black and white prints is crucial for quality results, but also for understanding the chemistry involved and potential hazards.
- Hypo (Sodium Thiosulfate): The primary component of fixer. Fumes are a key concern.
- Wetting Agents: These can be irritating to the skin.
Always read the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) – now commonly referred to as Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – for each chemical you use. These sheets provide detailed information on hazards, safe handling procedures, and first aid measures. It’s helpful to research the chemical’s properties and interactions to better anticipate any potential risks before starting your work. Understanding the nuances in chemical application, such as when using selenium toner, can also enhance image quality and archiving ability, while keeping safety as a high priority.
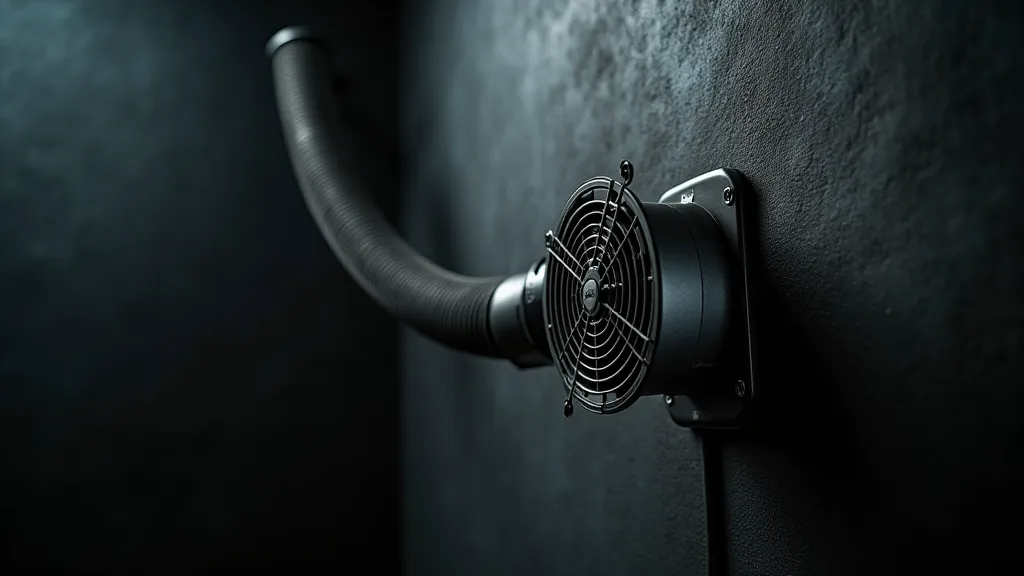
Ventilation Solutions for Your Darkroom
The ideal solution is a dedicated ventilation system, but even simple measures can make a significant difference. A well-ventilated space doesn’t just reduce chemical exposure; it also improves the overall working environment, making long hours in the darkroom more comfortable. Consider the size of your darkroom, the type of chemicals used, and the potential for fumes to accumulate when deciding on a ventilation solution.
- Natural Ventilation: Opening windows and doors is the simplest option, provided you have a clean airflow. This is often sufficient for small, well-located darkrooms. However, be mindful of external pollutants and humidity levels which can impact image quality and contaminate your chemicals.
- Exhaust Fans: A properly sized exhaust fan vented to the outside is an excellent choice. Consider the size of your darkroom and the volume of chemicals used to determine the appropriate fan capacity. Ensure the exhaust vents away from areas where people congregate or where air is recirculated.
- Air Purifiers: While not a substitute for ventilation, air purifiers with activated carbon filters can help to remove some chemical odors and particulate matter. These are often best used in conjunction with a ventilation system rather than as a primary solution.

Essential Safety Practices
Beyond ventilation, these safety practices are crucial. Remember that darkroom safety is an ongoing commitment, requiring constant vigilance and adherence to best practices.
- Gloves: Always wear chemical-resistant gloves when handling darkroom chemicals. Nitrile gloves are a good choice. Ensure gloves are of adequate thickness to prevent chemical permeation.
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses or goggles are essential to protect your eyes from splashes. Consider using a face shield for added protection when handling large volumes of chemicals.
- Protective Clothing: Wear clothing that you don’t mind getting stained. An apron is a good idea. Darkroom aprons are readily available, offering a convenient and protective barrier.
- Good Housekeeping: Keep your darkroom clean and organized. Promptly clean up spills. A clean workspace minimizes the risk of accidents and contamination.
- Proper Chemical Storage: Store chemicals in tightly sealed containers, away from heat and direct sunlight. Keep them out of reach of children and pets. Clearly label all containers to avoid accidental misuse.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of used chemicals responsibly. Do not pour them down the drain. Follow local regulations for chemical waste disposal. Diluting waste before disposal is often recommended, but *always* research specific guidelines for your area. Contact your local environmental agency for specific disposal instructions and permitted disposal sites.
- Print Masking Techniques: When performing dodging and burning, knowing how to making a print mask for precise dodging and burning will lead to better prints and minimize the amount of chemicals you need to use.
Advanced Considerations and Troubleshooting
Even with diligent safety measures, unexpected challenges can arise. Understanding potential issues and having contingency plans is a mark of an experienced darkroom technician. Chemical reactions can sometimes be unpredictable, so a solid understanding of chemistry is invaluable.
- Humidity Control: Excessive humidity can damage paper and chemicals. A dehumidifier might be necessary in some climates.
- Temperature Stability: Temperature fluctuations can affect development times and image quality. Maintaining a consistent temperature is ideal.
- Chemical Contamination: Even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a batch of prints. Use distilled or deionized water for mixing chemicals. Regularly clean your trays and tanks.
- Failing Equipment: Regularly inspect your equipment for leaks or malfunctions. Have backup equipment on hand if possible.
Final Thoughts
Creating stunning black and white photographs in the darkroom is an incredibly rewarding experience. However, it’s crucial to prioritize your health and safety. By understanding the potential hazards and implementing proper ventilation and safety practices, you can enjoy the craft for years to come without compromising your well-being. Always err on the side of caution and research specific guidelines for your local area. Remember, darkroom photography is about more than just technical skill; it's about responsible stewardship of your health and the environment.





